How suppliers in the oil and gas industry can contribute to the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a unanimous call for action by all countries of the world to promote prosperity while protecting the planet. The philosophy behind the SGDs recognizes that ending poverty is intricately linked with strategies that promote economic growth and address a broad range of social needs including health, education, social protection, and job creation. These strategies must be formulated while tackling climate change and ensuring environmental protection. This article presents a broad overview of the 17 SGDs and how the oil and gas industry can contribute to the realization of these goals. The policies and initiatives of an internationally established valve supplier to the oil and gas industry, AS-Schneider, for the realization of the 17 SGDS are presented and discussed.
What are the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)?
Sustainable Development Goals identify the most urgent problems of the world. They form a basis for international commitment and cooperation to address the interrelated issues of climate change, management of the world’s fragile natural resources, promotion of peace and inclusivity, reduction of inequality and ensuring prosperity of economies. Developed at the 2012 UN Conference on Sustainable Development, SDGs identified challenges that we face as humanity. In 2015, a set of 17 global goals, related to the environment, politics and world economy were agreed upon through a vote to drive the transformation of the world during the period 2015-2030.
The 17 SDGs are summarized below:

Source: www.sdgs.un.org/goals
Who are the Sustainability Goals for?
The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development recognizes that governments have the primary responsibility for implementing the SDGs in their respective countries. Governments must ensure implementation follow-up and review over the implementation period, at the national, regional and global levels. SDG-16 emphasizes that governments must “build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels” to achieve the SDGs.
The implementation process of the SDGs is also called localizing the SDGs. This means that in addition to the government, universities, the industry, institutions, independent organizations and individual people must work separately and jointly for the achievement of one or several goals. While governments mainly implement the goals through legislation, they must also form partnerships with academia, industry and other independent organizations to find new ways of shortening the path towards these goals. Finally, coordination between governments at the international level is also crucial. The SDGs emphasize the need for more well-to-do countries to partner with countries with access to limited financial resources.
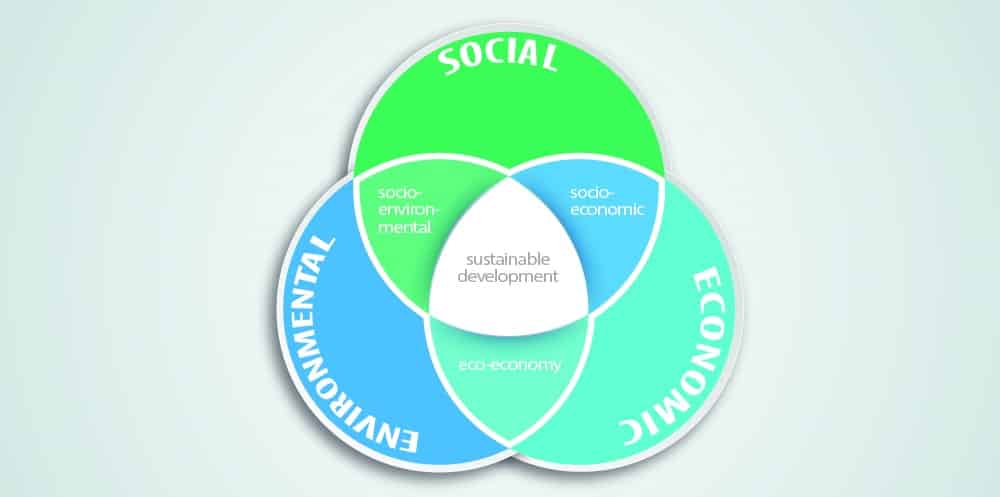
Note: Sustainable development is the intersection of social development, economic growth and environmental protection.
What is the relevance of the SDGs for business in general?
Business and industry have a key role to play in achieving the SDGs. Industrial development directly and indirectly supports several social objectives identified in the SDGs. These include employment generation, poverty eradication, social inclusion, gender equality, greater access to education, better health care and improved labor standards. SDG-9 sets the target to build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation through increased investment in scientific research and innovation. SDGs present an opportunity for leading companies to demonstrate how their business can help advance sustainable development, both by minimizing negative effects and maximizing positive contribution to the well-being of the people and the planet. Businesses must use the SDGs as a framework to shape and implement their strategies, goals and activities. Focus on implementing the SDGs can offer a range of benefits to businesses such as:
- Identifying future business opportunities
- Improved attractiveness as an employer
- Strengthening stakeholder relations and keeping the pace with policy developments
- Enhancing the value of corporate sustainability
- Stabilizing societies and markets
SDG Compass
The SDG Compass, published by the Global Compact, provides guidance, in 5 easy steps, to companies on how they can align their strategies and manage their contribution to the realization of the SDGs.
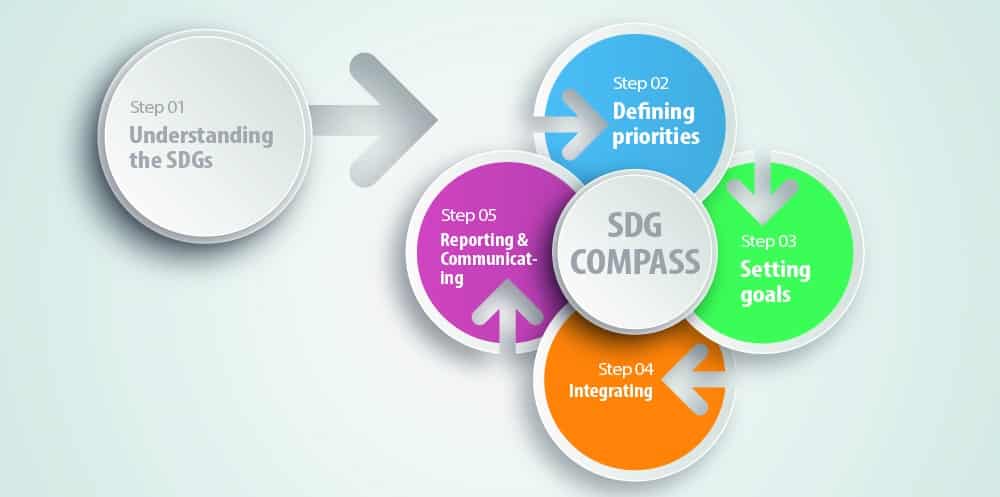
Note: The SDG Compass guides companies on how they can align their strategies and manage their contribution to the SGDs.
Step 01 - Understanding the SDGs
The first step for companies is to familiarize themselves with the SDGs.
Step 2 - Defining priorities
In the second step, companies define their priorities based on an assessment of their current and potential impact, across their value chains, on the SDGs.
Step 3 - Setting goals
In the third step, companies align their goals with the SDGs to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable development.
Step 4 - Integrating
The fourth step involves Integrating sustainability into company’s governance and core business along with setting sustainable development targets for all functions within the company. Companies engage in partnerships across the value chain, with governments, and with other organizations.
Step 5 - Reporting and communicating
In the final step, companies build SDGs into their communication with stakeholders and evaluate their performance with reference to sustainable development. These reports form the basis for redefining priorities and setting new goals.
What are the benefits of the SDGs for suppliers in the oil and gas industry?
The oil and gas sector has a central role to play in the realization of SDGs, it has the potential to impact, both positively and negatively, a range of areas covered by the SDGs. Oil and gas companies in their individual capacity and in collaboration with governments, communities, civil society and other partners, can contribute significantly to the achievement of the SDGs.
Historically, the oil and gas sector has contributed to some of the major issues that the SDGs seek to address, such as climate change, environmental degradation, population displacement, economic and social inequality, armed conflicts, and increased health risks. By enhancing its positive contributions and by mitigating negative impacts, the oil and gas industry has the potential to contribute to all 17 SDGs. Responsible oil and gas production can foster economic as well as social development by providing access to affordable energy, opportunities for employment, skills development, increased fiscal revenues, and improved infrastructure.
How can suppliers in the oil and gas industry contribute to SDGs?
The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and IPIECA, the global oil and gas industry association for environmental and social issues, have jointly developed an Atlas to map the oil and gas industry to the 17 SDG goals. The table below summarizes some of the key measures that oil and gas businesses can integrate into their core business strategy, and some steps that they can take in collaboration with stakeholders for the realization of SDGs.
SDG | Integrate into core business strategy | Collaborate and leverage |
|---|---|---|
1. SDG: No Property | • Increase access to energy
• Contribute to fiscal sustainability | • Community development agreements
• Reduce gender inequality |
2. SDG: Zero Hunger | • Align co-located agricultural and oil and gas development activities
• Shared-use infrastructure to enhance agricultural productive capacity | • Increase efficiency in oil and gas-based agricultural products |
3. SDG: Good Health and Well-being | • Conduct health impact assessments to strengthen capacity to manage health risks
• Reduce occupational risks | • Strengthen public health systems’ response to potential health risks and epidemics |
4. SDG: Quality Education | • Establish a company strategy for local content to promote sustainable development
• Invest in workforce education, training and technical programs | • Support in-country education and skills development efforts |
5. SDG: Gender Equality | • Develop gender-sensitive local content policies
• Support full and effective participation of women at all levels of decision-making | • Address negative social impacts including all forms of violence
• Enhance the use of STEM education to empower women in the oil and gas industry |
6. SDG: Clean Water and Sanitation | • Develop a company water strategy
• Understand water scarcity risk management
• Substantially increase water use efficiency | • Improve understanding of the water-energy nexus
• Participatory approach to water management
• Shared-use water infrastructure
|
7. SDG: Affordable and Clean Energy | • Improve access to energy services through shared infrastructure
• Grow the share of natural gas in the energy mix | • An integrated, multi-stakeholder approach to energy poverty |
8. SDG: Decent work and Economic Growth | • Conduct skills assessment and communicate reasonable expectations
• Foster full and productive local employment and workforce development | • Support economic diversification to achieve higher levels of economic productivity |
9. SDG: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure | • Upgrade infrastructure and technology to make them sustainable
• Evaluate potential opportunities for shared use infrastructure | • Enhance technological capabilities and knowledge transfer
• Expand off-grid energy access |
10. SDG: Reduced Inequalities | • Ensure full and transparent tax payments
• Assess inequality impacts in project planning | • Enhance revenue management and improve local governance |
11. SDG: Sustainable Cities and Communities | • Protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage
• Address risks related to operations in urban environments | • Coordinate planning for urban and regional development |
12. SDG: Responsible Consumption and Production | • Integrate product stewardship approach
• Introduce environmentally-sound and efficient chemical and waste management | • Coordinate approaches to sustainability |
13. SDG: Climate Action | • Plan strategically for a net-zero emissions future
• Self-assess carbon resiliency
• Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate change impacts
• Mitigate emissions within oil and gas operations | • Partner in research and development and education outreach
• Support effective policy measures
• Help consumers lower their emissions |
14. SDG: Life Below Water | • Incorporate environmental assessments into management plans
• Minimize and address the rate of ocean acidification | • Transfer and share marine technology
• Coordinate biodiversity research |
15. SDG: Life and Land | • Effective biodiversity and ecosystem management
• Implement the mitigation hierarchy | • Multi-stakeholder knowledge sharing
• A landscape-wide conservation approach |
16. SDG: Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions | • Integrate human rights perspective in impact assessments
• Community engagement and consent | • Improve institutions through NOCs
• Increase effective, accountable and transparent institutions |
17. SDG: Partnership for the Goals | • Build government capacity
• Develop and disseminate sustainable energy technologies | • Participate in dialogue
• Strengthen coordination between initiatives
• Incorporate SDGs into policies
|
Adapted from: Mapping the Oil and Gas Industry to the SDGs: An Atlas
How the AS-Schneider Group as a valve supplier to the oil and gas industry is contributing to the SDGs
As a socially and environmentally responsible company, AS-Schneider is committed to playing its role in the realization of all 17 SDGs. AS-Schneider aims to improve global infrastructure through production of reliable components, assist in environmental protection measures through technological advancements, and sustainably produce its products to limit their environmental impact. AS-Schneider strives to integrate the SDGs in its core business strategy. Following are some examples of how AS-Schneider has integrated SGDs into its core policies:
Environmental Policy (SDG-9, SDG-12, SDG-13)
AS-Schneider continuously improves its product design, processes and production methods to conserve resources and minimize emissions. The company uses energy-efficient and water-saving technologies to reduce waste prevention and invests in recycling. AS-Schneider has implemented an Environmental Management System according to the international standard DIN EN ISO 14001:2015 for continuous improvement in environmental performance and protection.
Anchoring in the Organization (SDG-7, SDG-13, SDG-15)
At its headquarters in Nordheim, AS-Schneider has designated a dedicated Environmental Protection Officer (EPO), to coordinate and manages all environmental measures. The EPO works in collaboration with the Hazardous Substance Officer, the Waste Management Officer, the Fire Protection Officer, the Health & Safety Officer, and the Energy Management Officer. The EPO leads the team that meets to discuss all environmentally relevant issues at regular intervals to initiate and monitor the necessary actions.
Occupational Health and Safety (SDG-3)
At AS-Schneider, all workplaces are designed to preventively protect the occupational health and safety of its employees. The employees are trained and constantly reminded of their personal responsibility for safely carrying out their tasks.
Involvement of Employees (SDG-4, SDG-13)
AS-Schneider encourages and motivates its employees to contribute to environmental protection with the management and executives serving as role models. All company employees are regularly updated on changes in its environmental policy and goals.
Diversity Management (SDG-5, SDG-10)
As a global company, AS-Schneider sees its pronounced internationalization as an opportunity to leverage interaction of different cultures, mindsets and talents for success. The company encourages continuous dialogue between its teams around the world and international subsidiaries. Intercultural workshops are organized to cultivate an open-minded and respectful team spirit. AS-Schneider has actively committed to the promotion of diversity in the Group as well as to building a respectful and fair working atmosphere by signing the Charter of Diversity.
Employee Responsibility (SDG-1, SDG-3, SDG-4, SDG-8)
AS-Schneider offers its employees individual opportunities for development and good future prospects through demand-oriented training programs as well as e-training and extensive introductory training sessions on numerous topics. It strives to adapt working conditions to the respective life situations of its employees so that they may strike an appropriate balance between work and their private lives.
Environmentally friendly production (SDG-6, SDG-12, SDG-13, SDG-14)
AS-Schneider uses energy-efficient processes, to produce resource-saving and environment-friendly products. The company is committed to introducing significant improvements in the handling of resources over the coming years to continuously implement better ways of protecting the environment that go far beyond the legal requirements like:
-
Environmentally friendly cleaning of parts:
AS-Schneider uses an innovative system to relubricate and clean the production parts after the working process. The energy consumption is reduced by approximately 40 percent compared to the old system with the same cleaning volume. -
100 percent recycling of cutting oil:
AS-Schneider has created a safer, more environment-friendly work environment by switching to a new cutting oil that no longer contains any dangerous substances. The change has led not only to a reduction in electricity consumption, but also to reduction in lubricating oil consumption of around 10,000 liters per year. -
Reduction in fugitive emissions:
All valves produced by AS-Schneider are subjected to the required actuation cycles and examined for the smallest leaks with helium mass spectrometers. Due to these rigorous endurance tests, AS-Schneider products help reduce fugitive emissions from production processes.
Conclusion
The targets mentioned in the 17 SGDs are ambitious especially in view of the time and resources lost due to the COVID-19 pandemic. In this context it is important for governments, institutions, organizations and individuals to make up for lost time and put in their maximum effort for the realization of these goals by the year 2030.
The oil and gas industry is at the center of the sustainability debate. It is essential for all players in the industry, big and small, to integrate the 17 SDGs in their core business strategy to help sustain our planet.

